Covid-19
The first case of the COVID-19 pandemic in India was reported on 30 January 2020, originating from China. As of 10 May 2020, the Ministry of Health and Family Welfare have confirmed a total of 62,939 cases, 19,358 recoveries (including 1 migration) and 2,109 deaths in the country. The infection rate of COVID-19 in India is reported to be 1.7, significantly lower than in the worst affected countries.The outbreak has been declared an epidemic in more than a dozen states and union territories, where provisions of the Epidemic Diseases Act, 1897 have been invoked, and educational institutions and many commercial establishments have been shut down. India has suspended all tourist visas, as a majority of the confirmed cases were linked to other countries.
On 22 March 2020, India observed a 14-hour voluntary public curfew at the instance of the prime minister Narendra Modi. The government followed it up with lockdowns in 75 districts where COVID-19 cases had occurred as well as all major cities. Further, on 24 March, the prime minister ordered a nationwide lockdown for 21 days, affecting the entire 1.3 billion population of India.On 14 April, the prime minister extended the ongoing nationwide lockdown till 3 May.
1st national wide lock down
23rd March to 13th April
2nd national wide lock down
On 14th April, the prime minister extended the ongoing nationwide lockdown till 3rd May.
3rd national wide lock down
5th May to extended the ongoing nationwide lockdown till 17th May 2020
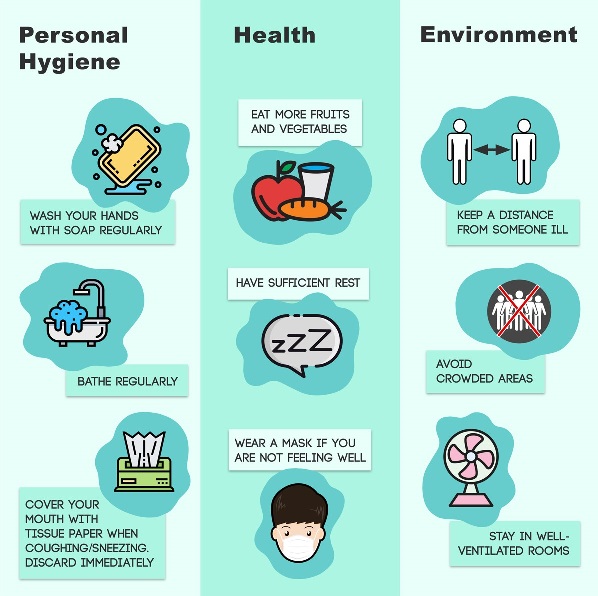
Precaution of Covid-19